« Get started now in order to find your perfect match | Main | Chat with girls online – find your perfect match now »
Debt Ratio: An In-Depth Examination of Financial Leverage
By admin | December 28, 2023
You are being directed to ZacksTrade, a division of LBMZ Securities and licensed broker-dealer. The web link between the two companies is not a solicitation or offer to invest in a particular security or type of security. ZacksTrade does not endorse or adopt any particular investment strategy, any analyst opinion/rating/report or any the debt ratio is used: approach to evaluating individual securities.
- Have you been exploring various financial metrics to gain insights into either your own company or a company you’re looking to invest in?
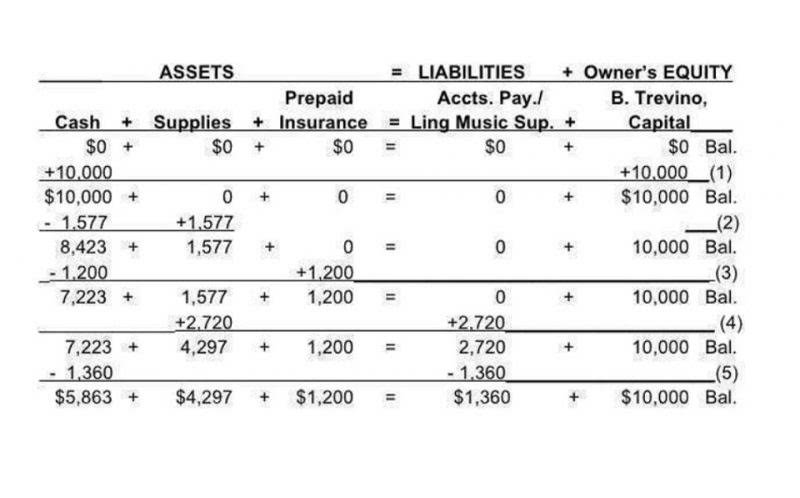
- Tesla had total liabilities of $30,548,000 and total shareholders’ equity of $30,189,000.
- The debt ratio shows the overall debt burden of the company—not just the current debt.
- The debt ratio is important because it indicates a company’s leverage and its level of financial risk related to the amount of money borrowed to fund daily operations.
- His work has been featured by USA TODAY, Washington Post, Bankrate, CBS News, and Fox Business.
Debt Ratio: Interpreting, Calculating, and Optimizing Financial Health
Conversely, if the D/E ratio is too low, managers may issue more debt or repurchase equity to increase the ratio. Another example is Wayflyer, an Irish-based fintech, which was financed with $300 million by J.P. The following figures have been obtained from the balance sheet of XYL Company. Pete Rathburn is a https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc copy editor and fact-checker with expertise in economics and personal finance and over twenty years of experience in the classroom.

Debt Ratio Formula
Additionally, it is important to compare a company’s debt ratio to industry averages and competitors to gain a better understanding of its financial health and position in the market. Changes in long-term debt and assets tend to affect the D/E ratio the most because the numbers involved tend to be larger than for short-term debt and short-term assets. If investors want to evaluate a company’s short-term leverage and its ability to meet debt obligations that must be paid over a year or less, they can use other ratios. Conversely, during periods of economic growth, a high debt ratio may not necessarily be a red flag. In a bullish market, companies often borrow to fund expansion plans and business growth.
What is Account Analysis in Accounting: Charges and Example
But generally a debt ratio of 0.4 or below is considered to be favorable and as it suggests a lower reliance on debt. This means that 37.5% of the company’s assets are financed by debt, providing insight into its financial leverage and risk level. It’s great to compare debt ratios across companies; however, capital intensity and debt needs vary widely across sectors. The financial health of a firm may not be accurately represented by comparing debt ratios across industries. Bear in mind how certain industries may necessitate higher debt ratios due to the initial investment needed. Paying off your credit cards with the highest interest rates first is known as the debt avalanche method.

What Certain Debt Ratios Mean
Utilities and financial services typically have the highest D/E ratios, while service industries have the lowest. On the other hand, when a company sells equity, it gives up a portion of its ownership stake in the business. The investor will then participate in the company’s profits (or losses) and will expect to receive a return on their investment for as long as they hold the stock. The debt capital is given by the lender, who only receives the repayment of capital plus interest.

Each business requires a unique strategy, depending on its specific circumstances and challenges. Every decision on a company’s debt ratio comes with its own set of rewards and risks. A high debt ratio might provide more resources for growth and expansion, but it also brings potential financial risk if the borrowing company struggles to repay the debt. For example, a utility or consumer staple company could have a much higher debt ratio than a highly cyclical industrial company. However, the utilities and consumer staples tend to have much less volatile earnings and more reliable cash flows from one year to the next.
How Can the D/E Ratio Be Used to Measure a Company’s Riskiness?
- It is important to evaluate industry standards and historical performance relative to debt levels.
- Companies unable to service their own debt may be forced to sell off assets or declare bankruptcy.
- As a result, drawing conclusions purely based on historical debt ratios without taking into account future predictions may mislead analysts.
- A higher value will mean the entity is more likely to default and may turn bankrupt in the long run.
- It also indicates financial health and flexibility, allowing you to save more and manage unexpected expenses.
Ultimately, the acceptable debt ratio depends on what the standard is for that industry. Lenders often have debt ratio limits and do not extend credit to over-leveraged companies. A steadily rising D/E ratio may make it harder for a company to obtain financing in the future. The growing reliance on debt could eventually lead to difficulties in servicing the company’s current loan obligations. Very high D/E ratios may eventually result in a loan default or bankruptcy. In the banking and financial services sector, a relatively high D/E ratio is commonplace.
- This is a particularly thorny issue in analyzing industries notably reliant on preferred stock financing, such as real estate investment trusts (REITs).
- Higher D/E ratios can also tend to predominate in other capital-intensive sectors heavily reliant on debt financing, such as airlines and industrials.
- But before that, let’s prepare ourselves for the process of deciphering the implications of different debt ratios.
- Lenders, including banks and other credit institutions, often use the debt ratio as a fundamental component in their decision-making process.
- This conservative financial stance might suggest that the company possesses a strong financial foundation, has lower financial risk, and might be more resilient during economic downturns.
Make sure you use the total liabilities and the total assets in your calculation. The debt ratio shows the overall debt burden of the company—not just the current debt. A company that has a debt ratio of https://www.bookstime.com/articles/minimum-wage-and-overtime-pay more than 50% is known as a “leveraged” company. Improving a company’s debt ratio may involve steps like enhancing cash flows, reducing unnecessary expenses, or restructuring existing debts.
Topics: Bookkeeping | Comments Off
Comments are closed.